Recombining capital assets for increased returns and increased profit.

This news article from www.telegraph.co.uk details how recombination and reallocation of capital resulted in an increase in ROC (Return On Capital) from 5 per cent to 8 percent, resulting in the potential for “double digit” profit growth.
——————————————————————————————————————————————————-
One of capitalism’s paradoxes is that the arrival of new competitors can make incumbent businesses stronger.
When the craft brewing revolution began a decade or so ago, some saw the proliferation of small, local, individualistic beer brands as a huge threat to the drab monoliths that sold the same globally advertised beers in every corner of the world. But it hasn’t turned out that way.
“Some people still say craft beers threaten the bigger players,” says Michael Crawford of Chawton Global Investors. “But it’s fairly easy for the incumbents to offer craft beers themselves by acquiring smaller brewers or by creating their own brands.
“The craft beer movement has also re-energised the whole beer market. People were bored with the old brands and many had experimented with switching to wine. Craft beers renewed their interest.”
In the absence of existential competitive threats, being a global beer maker is a ticket to strong financial returns, Crawford says. “Once you have built an operation of a decent size in a particular country you benefit from economies of scale and use your brands to protect yourself from commodity pricing,” he adds.
Which of the global brewers offers the best prospects? Crawford says AB InBev, which has 29pc of the world market thanks to a series of big acquisitions, is actually too big and suffers from “diseconomies of scale”. “Investors currently seem to see Heineken as the strongest ‘underdog’ but I think it has deteriorated a little in management quality recently. So my pick it Carlsberg,” he says.
It too had lost its way but a chief executive brought in six years ago has executed “a classic turnaround” and restored the firm’s profitability.
“Carlsberg had a strong base: it was the market leader or number two in much of western Europe, it was very strong in Russia, Ukraine and other east European countries and was well placed in China, India and Vietnam,” Crawford says. “But its previous bosses were guilty of poor capital allocation.
“It was earning about 5pc returns on capital and had no proper strategy to improve matters. Then in 2015 it made Cees ’T Hart its new boss. He was a Unilever veteran and also had the turnaround of a Danish beverage firm under his belt. He put in place a multi-stage recovery strategy at Carlsberg.
“First he brought the company’s infrastructure up to date. The firm had inherited lots of old, inefficient breweries. He rationalised, selling off some valuable land in the process, so that a single site, with the most modern and efficient equipment, could take the place of four or five previously. Then he started to pay off some of its debts. He also brought in more capable management, tapping other staples companies such as Unilever.”
The next step was to divide the portfolio in two. In the more mature markets he sought to sell more premium products as opposed to increasing volumes. The craft movement played to this strategy, although he also promoted low-alcohol beer, another fast growing area. “This pushed up average prices without increasing volumes so returns on capital started to rise,” Crawford says.
The other half of the portfolio was the genuine growth markets of China, India and Vietnam. “In China it had a strong position in the west of the country thanks to its WuSu brand and was able to spread eastwards via digital campaigns. In India it used its 60pc-plus market share in neighbouring Nepal as a foundation. It is number four in Vietnam but it’s a fast-growing market,” the fund manager says.
In Russia he says the strategy is to protect market share, maintain returns and use its “cash cow” status to help fund growth elsewhere. Such growth means that Russia is becoming a smaller part of the business.
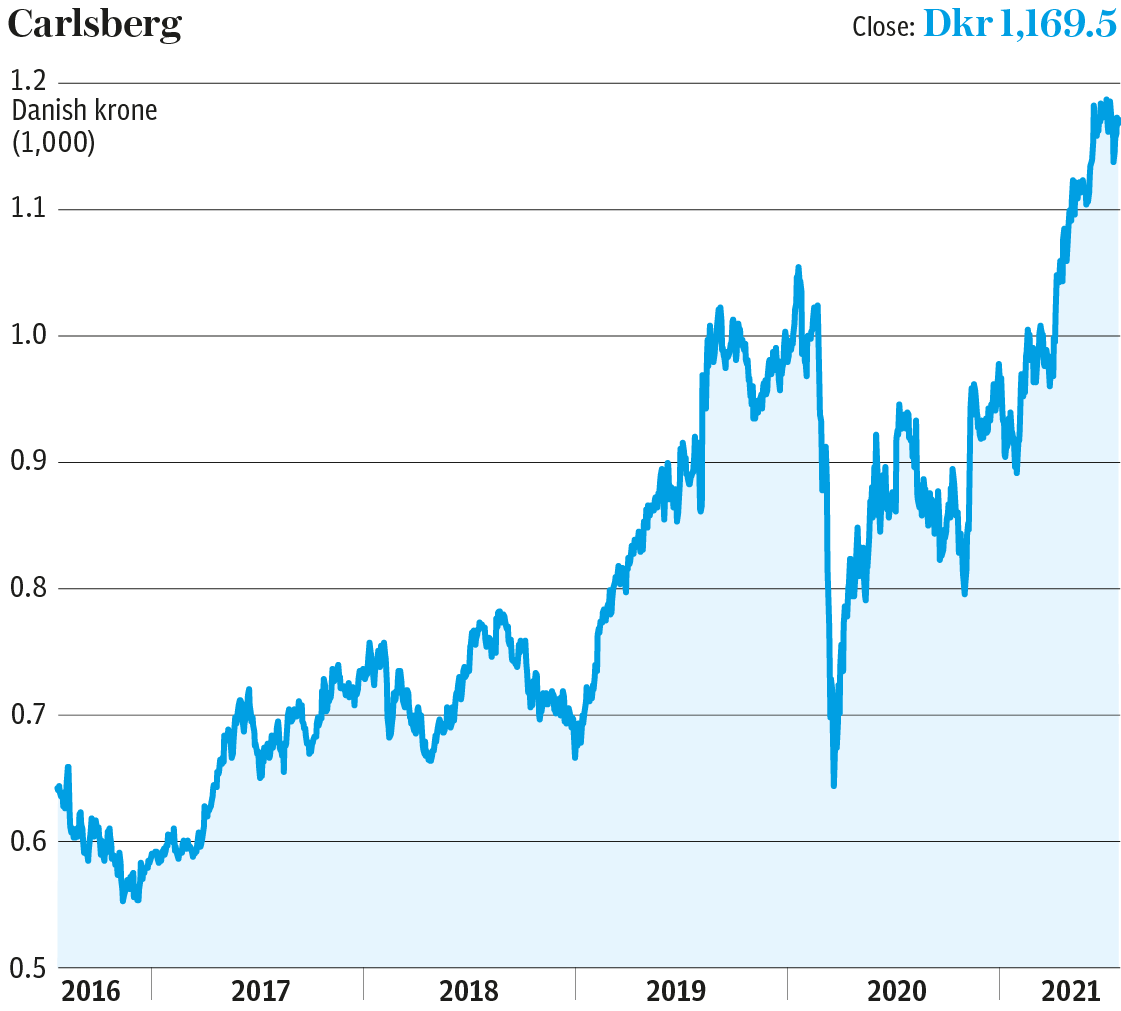
“The return on capital is now 8pc and I think it would have been 10pc last year but for the virus, which hit sales and profits,” Crawford adds. “All in all this has been a classic turnaround – and when you are in a relatively attractive industry anyway a turnaround can be quite effective.”
He says he expects double-digit profit growth over the next few years, which makes the Copenhagen-listed shares’ multiple of about 22 times predicted earnings for 2022 look fair.






Responses