How Murray Rothbard’s Theory of Entrepreneur-Driven Progress Can Be Applied to Modern Businesses
Recently, on the Human Action Podcast, Jeff Deist and I discussed the Rothbardian theory of the entrepreneurial economy in chapter 8 of Man, Economy, and State, titled “Production, Entrepreneurship, and Change.” In this article I will illustrate just how this Austrian theory is applied effectively in the business world.
In chapter 8, Rothbard establishes the principles of what he calls the progressing economy, one in which gross investment in capital goods is increasing, productivity is growing, and firms are making profits, indicating social affirmation that they are deploying resources in the ways best adjusted to the most urgent and evolving consumer needs. Specifically, firms are making an economic profit—returns higher than the going rate of interest derived from social time preference.
Importantly, economic profits (returns higher than the cost of capital) are hard to achieve and even harder to maintain. Rothbard points out that, to succeed in this challenge, entrepreneurs must demonstrate superior foresight and judgment, and practice continuous dynamic improvement in their assembly and reassembly of assets to serve the consumer. This urgency is sharpened by the competition of new entrepreneurs who see the high returns that the pioneering entrepreneur has achieved and are willing to enter the same space for lower margins so long as returns remain higher than the going interest rate. Eventually, all the superior returns will be competed away—unless the first entrepreneur keeps changing and advancing to serve more and higher-valued consumer needs.
More specifically, Rothbard’s construct is that economic profit is the result of entrepreneurs identifying discrepancies in the capital structure where capital is overdeployed in the service of less acutely felt consumer wants and underdeployed in the service of some more acutely felt consumer wants. The function of entrepreneurship is to make the adjustment that consumers are demanding. Entrepreneurs buy factors that are underpriced because of the discrepancy and recombine them to serve currently underserved needs. The adjustments are always in the direction of higher and higher productivity. The prices of the new consumer goods and services generate a profit and a return that is higher in the new, adjusted arrangement of factors than in the prior arrangements.
Rothbard also deduces that the economic profit margin will erode over time because more entrepreneurs, seeing the high return for the new arrangement, will enter the economic space and compete away the high returns, pulling them down toward the going interest rate. Entrepreneurs must continue to find more new urgent consumer needs to address, rearrange their capital structure even further, and maintain a continuous dynamism both in their capital structure and in their consumer offerings.
Man, Economy, and State is a treatise of Austrian economic theory. To what extent is it translatable to and applicable to the realities of business in 2020? The answer is that Rothbard’s acute theoretical insights can be applied directly in business strategy to great effect.
A recent McKinsey Insights article confirms every one of Rothbard’s theoretical points in real-world analysis.
First, the McKinsey consultants confirm the challenges inherent in the effort to achieve economic profit. Their S-curve distribution (they call it a “power curve” for marketing purposes) illustrates how very few firms make high economic returns and most hover close to, or in some cases below, the break-even (i.e., zero economic profit) line.
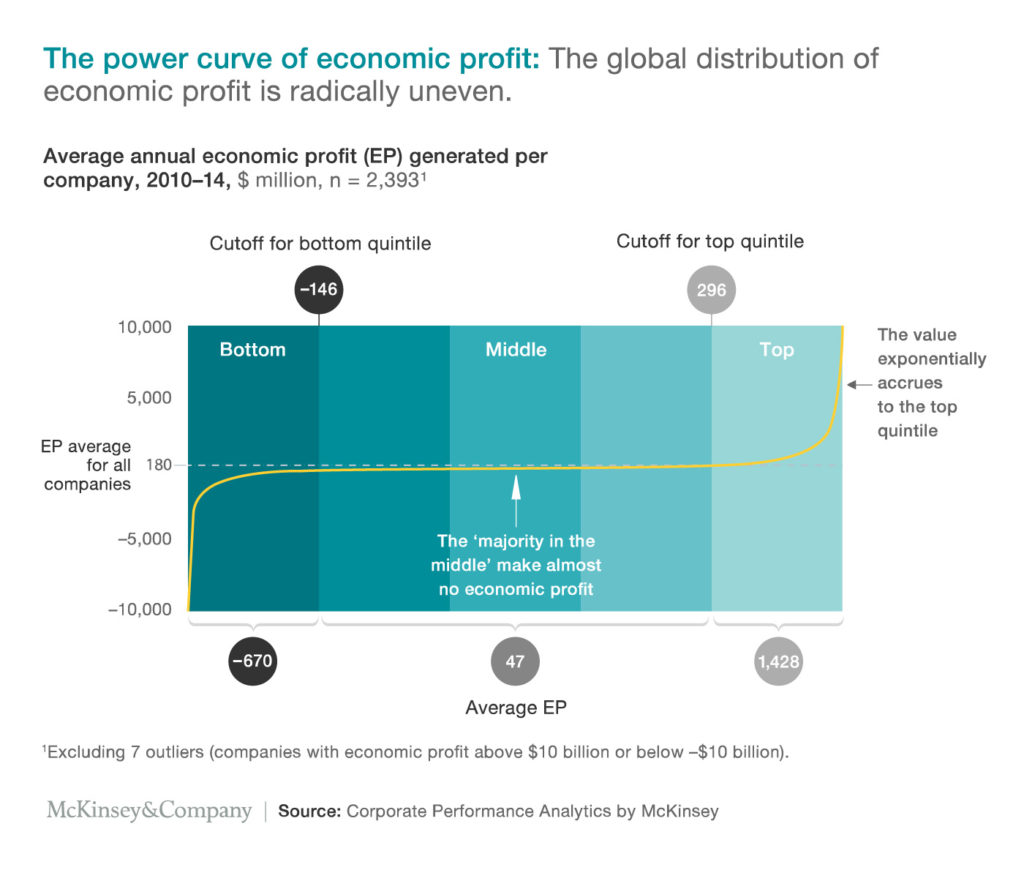
The McKinsey consultants conclude that:
- Market forces are pretty efficient. The average company in our sample generates returns that exceed the cost of capital by almost two percentage points, but the market is chipping away at those profits. That brutal competition is why you struggle just to stay in place. For companies in the middle of the power curve, the market takes a heavy toll. Companies in those three quintiles delivered economic profits averaging just $47 million a year.
- The curve is extremely steep at the bookends. Companies in the top quintile capture nearly 90 percent of the economic profit created, averaging $1.4 billion annually. In fact, those in the top quintile average some 30 times as much economic profit as those in the middle three quintiles, while the bottom 20 percent suffer deep economic losses. That unevenness exists within the top quintile, too. The top 2 percent together earn about as much as the next 8 percent combined. At the other end of the curve, the undersea canyon of negative economic profit is deep—though not quite as deep as the mountain is high.
With further data analysis, the McKinsey consultants identify the strategic actions that need to be taken to place a firm in the highest echelons of economic returns in their industry—and they confirm all the implications of Rothbardian theory. They propose five strategies of adjustment that effectively derive directly from Austrian theory.
First, they confirm the importance of continuous dynamic reallocation of resources by firms in order to achieve high returns.
Winning companies reallocate capital expenditures at a healthy clip, feeding the units that could produce a major move up the power curve while starving those unlikely to surge. The threshold here is reallocating at least 50 percent of capital expenditure among business units over a decade. When Frans van Houten became Philips’ CEO in 2011, the company began divesting itself of legacy assets, including its TV and audio businesses. After this portfolio restructuring, Philips succeeded at reinvigorating its growth engine by reallocating resources to more promising businesses (oral care and healthcare were two priorities) and geographies. Philips started, for example, managing performance and resource allocations at the level of more than 340 business-market combinations, such as power toothbrushes in China and respiratory care in Germany. That led to an acceleration of growth, with the consumer business moving from the company’s worst-performing segment to its best-performing one within five years.
They also identify an accompanying strategy for dynamic allocation of resources in the form of frequent M&A (mergers and acquisitions) activity—buying new assets and selling old ones. They call this strategy programmatic M&A: continuously buying and selling capital assets and turning over factors to dynamically manage capabilities.
You need a steady stream of deals every year, each amounting to no more than 30 percent of your market cap but adding over ten years to at least 30 percent of your market cap. Corning, which over the course of a decade moved from the bottom to the top quintile of the power curve, shows the value of disciplined M&A. Corning understands that doing three deals a year means it must maintain a steady pipeline of potential targets, conduct due diligence on 20 companies, and submit about five bids.
Beyond reallocation and M&A, strong capital expenditure is required to maintain profits.
You meet the bar on this lever (strong capital expenditures) if you are among the top 20 percent in your industry in your ratio of capital spending to sales. That typically means spending 1.7 times the industry median. Taiwanese semiconductor manufacturer Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) pulled this lever when the Internet bubble burst and demand for semiconductors dropped sharply. The company bought mission-critical equipment at the trough and was ready to meet the demand as soon as it came back. TSMC had been in a head-to-head race before the downturn but pulled clear of the competition after it ended because of its investment strategy. That laid the foundation for TSMC to become one of the largest and most successful semiconductor manufacturing pure plays in the world.
In addition, it is critical to maintain a strong productivity program.
This means improving productivity at a rate sufficient to put you at least in the top 30 percent of your industry. Global toy and entertainment company Hasbro successfully achieved the top quintile of the power curve with a big move in productivity. Following a series of performance shortfalls, Hasbro consolidated business units and locations, invested in automated processing and customer self-service, reduced head count, and exited loss-making business units. The company’s selling, general, and administrative expenses as a proportion of sales fell from an average of 42 percent to 29 percent within ten years. Sales productivity lifted, too—by a lot. Over the decade, Hasbro shed more than a quarter of its workforce yet still grew revenue by 33 percent.
The fifth strategic lever is improvements in differentiation. Modern Austrian economics identifies the importance of differentiation in Per Bylund’s islands of specialization theory and our focus on brand uniqueness as a source of superior profits. McKinsey uses gross margin as a proxy for differentiation, and their consultants say:
For business-model innovation and pricing advantages to raise your chances of moving up the power curve, your gross margin needs to reach the top 30 percent in your industry. German broadcaster ProSieben moved to the top quintile of the power curve by shifting its model for a new era of media. For example, it expanded its addressable client base by using a “media for equity” offering for customers whose business would significantly benefit from mass media but who couldn’t afford to pay with cash. Some of ProSieben’s innovations were costly, sometimes even cannibalizing existing businesses. But, believing the industry would move anyway, the company decided that experimenting with change was a matter of survival first and profitability second. ProSieben’s gross margin expanded from 16 percent to 53 percent during our research period.
Each one of these Rothbard-derived strategies can be effective in driving superior returns. Even more effective is to combine them, a recommendation with which Rothbard would concur.
Big moves are most effective when done in combination—and the worse your endowment or trends, the more moves you need to make. For companies in the middle quintiles, pulling one or two of the five levers more than doubles their odds of rising into the top quintile, from 8 percent to 17 percent. Three big moves boost these odds to 47 percent. To understand the cumulative power of big moves, consider the experience of Precision Castparts Corp. (PCC). In 2004, the manufacturer of complex metal components and products for the aerospace, power, and industrial markets was lumbering along. Its endowment was unimpressive, with revenues and debt levels in the middle of the pack, and the company had not invested heavily in R&D [research and development]. PCC’s geographic exposure was also limited, though the aerospace industry experienced enormous tailwinds over the following ten years, which helped a lot.
Most important, however, PCC made big moves that collectively shifted its odds of reaching the top quintile significantly. The company did so by surpassing the high-performance thresholds on four of the five levers. For mergers, acquisitions, and divestments, it combined a high value and large volume of deals between 2004 and 2014 through a deliberate and regular program of transactions in the aerospace and power markets.
PCC also reallocated 61 percent of its capital spending among its three major divisions, while managing the rare double feat of both productivity and margin improvements—the only aerospace and defense company in our sample to do so. While nearly doubling its labor productivity, PCC managed to reduce its overhead ratio by three percentage points. It lifted its gross profit-to-sales ratio from 27 to 35 percent.
The combination of a positive industry trend and successful execution of multiple moves makes PCC a showcase of a “high odds” strategy and perhaps explains why Berkshire Hathaway agreed in 2015 to buy PCC for $37.2 billion. Could our model have predicted this outcome? Based on the moves PCC made, its odds of rising to the top were 76 percent.
McKinsey’s reputation in business strategy consulting is second to none. To see these consultants apply Austrian economic theory so directly in their recommendations is a strong confirmation of its value.
This article was originally published by Hunter Hastings on Mises Wire





Responses